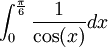הבדלים בין גרסאות בדף "חשבון אינפיניטיסימלי 2 - פתרון מועד א תשע"ג"
Ofekgillon10 (שיחה | תרומות) |
Ofekgillon10 (שיחה | תרומות) |
||
| שורה 69: | שורה 69: | ||
<math>x+\frac{2}{3}\ln|x-1|-\frac{1}{3}\ln|x^2+x+1|-\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\arctan\frac{2x+1}{\sqrt{3}}+c</math> | <math>x+\frac{2}{3}\ln|x-1|-\frac{1}{3}\ln|x^2+x+1|-\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\arctan\frac{2x+1}{\sqrt{3}}+c</math> | ||
| + | =שאלה 3= | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==סעיף א== | ||
| + | |||
| + | צריך לבדוק אם <math>\int_1^\infty \sin\sqrt{x}dx</math> מתכנס או מתבדר. | ||
| + | |||
| + | הצעה לפתרון: ננסה לחשב את <math>\lim_{b\to\infty} \int_1^b \sin \sqrt{x} dx</math>. נסתכל על <math>\int \sin\sqrt x dx</math>. ע"י החלפת משתנים נקבל <math>\sqrt{x}=t \Rightarrow \frac1{2\sqrt x} dx = dt \Rightarrow dx=2tdt</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | קיבלנו <math>\int 2t\sin t dt</math>. ניתן לראות ע"י אינטגרציה בחלקים (<math>u=2t, v'=\sin t</math>) כי האינטגרל הוא <math>2\sin(t)- 2t\cos t + C</math> ולכן מתקיים: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\lim_{b\to\infty} \int_1^\infty \sin\sqrt x dx = \lim_{b\to\infty} (2\sin\sqrt b - 2\sqrt{b}\cos\sqrt{b})-(2\sin1-2\cos1)</math> וזה כמובן לא מתכנס ולכן האינטגרל מתבדר | ||
=שאלה 4= | =שאלה 4= | ||
גרסה מ־18:31, 9 ביולי 2013
תוכן עניינים
שאלה 2
סעיף א
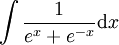
נציב 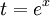 ואז
ואז 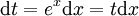
לאחר הצבה נקבל
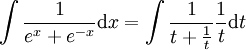
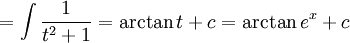
סעיף ב
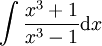
על ידי חילוק פולינומים קל לראות ש
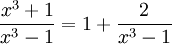
אז נתמקד בחישוב 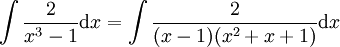
לפי האלגוריתם לחישוב אינטגרל של פונקציה רציונאלית נחפש
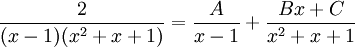
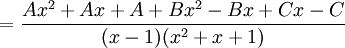
כלומר קיבלנו מערכת משוואות
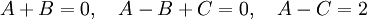
וקל לראות שהפתרון שלה הוא:
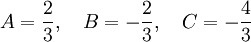
ברור ש
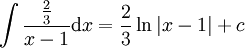
נותר לחשב את 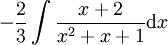
לפי השלמה לריבוע
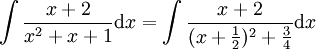
נבצע הצבה 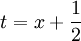 (רק בשביל נוחות) ואז נישאר עם
(רק בשביל נוחות) ואז נישאר עם
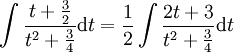
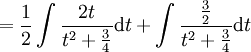
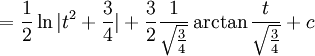
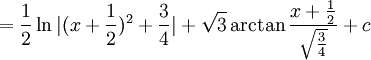
ולכן 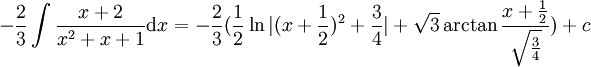
אם נסכום את כל מה שקיבלנו נקבל שהתוצאה היא
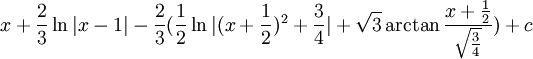
ואם מסדרים את זה יוצא
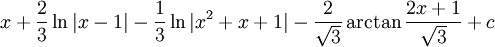
שאלה 3
סעיף א
צריך לבדוק אם 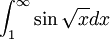 מתכנס או מתבדר.
מתכנס או מתבדר.
הצעה לפתרון: ננסה לחשב את 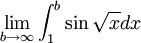 . נסתכל על
. נסתכל על 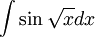 . ע"י החלפת משתנים נקבל
. ע"י החלפת משתנים נקבל 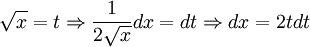
קיבלנו 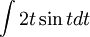 . ניתן לראות ע"י אינטגרציה בחלקים (
. ניתן לראות ע"י אינטגרציה בחלקים (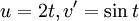 ) כי האינטגרל הוא
) כי האינטגרל הוא 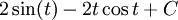 ולכן מתקיים:
ולכן מתקיים:
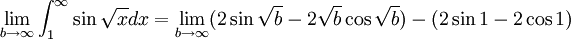 וזה כמובן לא מתכנס ולכן האינטגרל מתבדר
וזה כמובן לא מתכנס ולכן האינטגרל מתבדר
שאלה 4
הפרכה: ניקח את 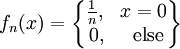 . נראה כי
. נראה כי 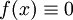 וההתכנסות היא במ"ש (קל להוכיח).
וההתכנסות היא במ"ש (קל להוכיח).
עוד פונקציה שמפריכה היא 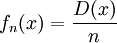 כאשר
כאשר 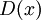 היא פונקציית דיריכלה. זאת אומרת,
היא פונקציית דיריכלה. זאת אומרת, 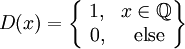
שאלה 6
נזכור כי הנוסחה לחישוב אורך עקומה של 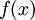 בקטע
בקטע ![[a,b]](/images/math/2/c/3/2c3d331bc98b44e71cb2aae9edadca7e.png) היא
היא 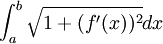 ולכן אנחנו מחפשים את
ולכן אנחנו מחפשים את 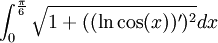 .
.
מתקיים: 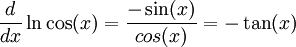 .
.
כמו כן, 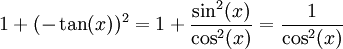 .
.
נראה כי ![\forall x \in [0,\frac{\pi}6] :\cos(x)>0](/images/math/5/4/b/54b0597ecf8483c39709d1da04d1f694.png) ולכן
ולכן 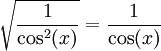 ולא צריך לדאוג לגבי הסימן המכנה.
ולא צריך לדאוג לגבי הסימן המכנה.
נרצה לחשב כעת את