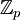הבדלים בין גרסאות בדף "משתמש:איתמר שטיין"
מתוך Math-Wiki
איתמר שטיין (שיחה | תרומות) |
איתמר שטיין (שיחה | תרומות) (←סעיף א) |
||
| שורה 4: | שורה 4: | ||
==שאלה 3== | ==שאלה 3== | ||
| − | == | + | ==שאלה 4== |
| − | <math>a_n | + | ראשית נשים לב שמשפט לייבניץ לא עובד כאן. כי לייבניץ דורש (בין השאר) ש <math>a_n</math> היא סדרה מונוטונית יורדת. |
| + | את הטענה ניתן להפריך. | ||
| − | + | נבחר | |
| − | + | <math>a_n=(-1)^{n+1}\frac{1}{n}</math> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | אזי בוודאי מתקיים | |
| − | + | <math>\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty} a_n=0</math> | |
| − | + | אבל | |
| − | <math>\ | + | <math>\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} (-1)^{n+1} a_n=\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}(-1)^{2n+2}\frac{1}{n}=\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}\frac{1}{n}</math> |
| − | + | שהוא טור מתבדר. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
גרסה מ־20:22, 29 בינואר 2013
שאלה 3
שאלה 4
ראשית נשים לב שמשפט לייבניץ לא עובד כאן. כי לייבניץ דורש (בין השאר) ש 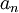 היא סדרה מונוטונית יורדת.
היא סדרה מונוטונית יורדת.
את הטענה ניתן להפריך.
נבחר
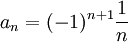
אזי בוודאי מתקיים
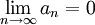
אבל
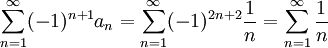
שהוא טור מתבדר.